GitLab Geo High Availability
This document describes a possible configuration on how to set up Geo in a Highly Available environment. If your HA setup differs from the one described in this document, you still can use the instructions and adapt them to your needs.
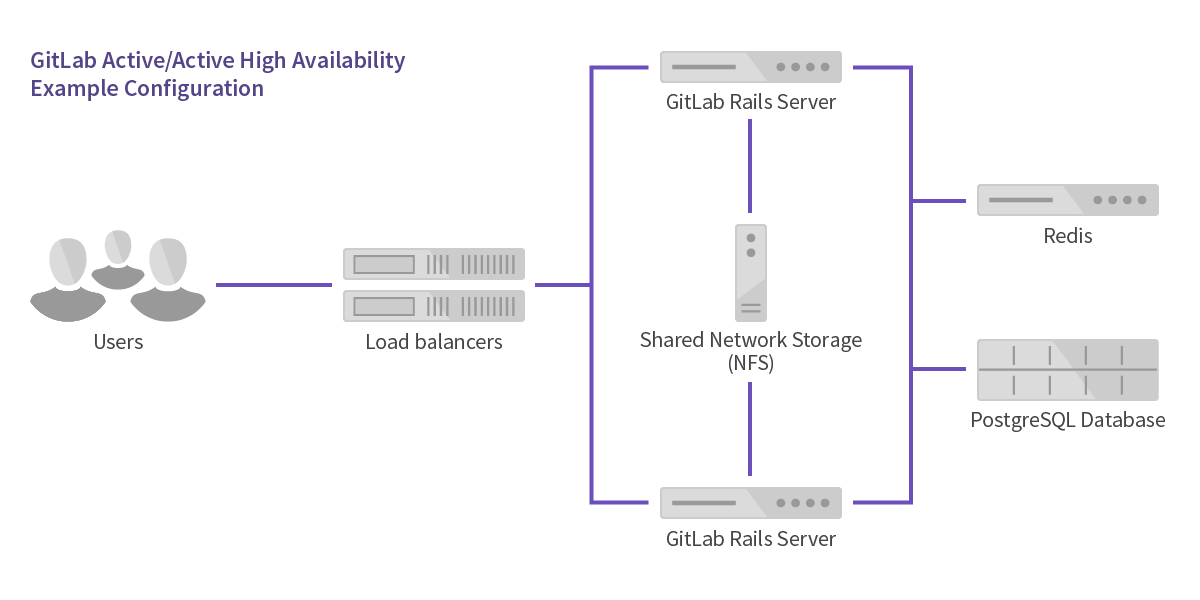
Architecture overview
This documentation assumes all machines used in this HA setup can communicate over the network using internal IP addresses.
NOTE: Note:
external_url must be the same for every machine, and https should be used.
Services machine
One machine, called the Services machine will be used to run:
- NFS shares
- PostgreSQL
- Redis
- HAProxy
Prerequisites
Make sure you have GitLab EE installed using the Omnibus package.
The following steps should be performed in the Services machine. SSH to it and login as root:
sudo -iStep 1: Set up NFS share
-
Install the required NFS packages:
apt-get install nfs-kernel-server -
Create the required directories:
mkdir -p /var/opt/gitlab/nfs/builds/ \ /var/opt/gitlab/nfs/git-data/ \ /var/opt/gitlab/nfs/shared/ \ /var/opt/gitlab/nfs/uploads/ -
Make the directories available through NFS, by adding this to
/etc/exports(see also the NFS HA recommended options):/var/opt/gitlab/nfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash) -
Start the NFS service:
systemctl start nfs-kernel-server.service -
Apply the settings to take effect:
exportfs -a
Step 2: Set up PostgreSQL server
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add the following:postgresql['enable'] = true ## ## Replace 1.2.3.4 with the internal IP address of the current machine and ## 2.3.4.5 and 3.4.5.6 with the internal IP addresses of the machines ## running the Application server(s). ## postgresql['listen_address'] = '1.2.3.4' postgresql['trust_auth_cidr_addresses'] = ['1.2.3.4/32', '2.3.4.5/32', '3.4.5.6/32'] gitlab_rails['auto_migrate'] = true gitlab_rails['db_password'] = 'DB password' -
Only for secondary nodes Also add this to
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:geo_postgresql['enable'] = true ## ## Replace 1.2.3.4 with the internal IP address of the current machine and ## 2.3.4.5 and 3.4.5.6 with the internal IP addresses of the machines ## running the Application server(s). ## geo_postgresql['listen_address'] = '1.2.3.4' geo_postgresql['trust_auth_cidr_addresses'] = ['1.2.3.4/32', '2.3.4.5/32', '3.4.5.6/32'] geo_secondary['auto_migrate'] = true geo_secondary['db_host'] = '1.2.3.4' geo_secondary['db_password'] = 'Geo tracking DB password'
Step 3: Set up Redis
Edit /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb and add the following:
redis['enable'] = true
redis['password'] = 'Redis password'
##
## Replace 1.2.3.4 with the internal IP address of the current machine
##
redis['bind'] = '1.2.3.4'
redis['port'] = 6379
##
## Needed because 'gitlab-ctl reconfigure' runs 'rake cache:clear:redis'
##
gitlab_rails['redis_password'] = 'Redis password'Step 4: HAProxy
We'll be using HAProxy to balance the load between the Application machines.
-
Manually stop Nginx (we will disable it in
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rblater):gitlab-ctl stop nginx -
Install the HAProxy package:
apt-get install haproxy -
Make sure you have a single SSL
pemfile containing the certificate and the private key.cat /etc/ssl/cert.pem /etc/ssl/privkey.pem > /etc/ssl/aio.pem -
Edit
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgand overwrite it with the following:global log 127.0.0.1 local0 log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice maxconn 4096 user haproxy group haproxy daemon defaults log global mode http option httplog option dontlognull option forwardfor option http-server-close stats enable stats uri /haproxy?stats frontend www-http bind *:80 reqadd X-Forwarded-Proto:\ http default_backend www-backend frontend www-https bind 0.0.0.0:443 ssl crt /etc/ssl/aio.pem reqadd X-Forwarded-Proto:\ https default_backend www-backend backend www-backend redirect scheme https if !{ ssl_fc } balance leastconn option httpclose option forwardfor cookie JSESSIONID prefix ## ## Enter the IPs of your Application servers here ## server nodeA 2.3.4.5:80 cookie A check server nodeB 3.4.5.6:80 cookie A check -
Start the HAProxy service:
service haproxy start
Step 5: Apply settings
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add the following:nginx['enable'] = false sidekiq['enable'] = false unicorn['enable'] = false ## ## These are optional/untested/irrelevant ## gitaly['enable'] = false gitlab_workhorse['enable'] = false mailroom['enable'] = false prometheus['enable'] = false Reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect.
-
Until Omnibus#2797 gets fixed, you will need to manually restart PostgreSQL:
gitlab-ctl restart postgresql geo-postgresql
Step 6: Step up database replication
Database replication will operate between the Services machines. Follow the Setup the database replication instructions to set up.
Application machine
Repeat these steps for every machine running gitlab-rails.
The following steps should be performed in the Application machine. SSH to it and login as root:
sudo -iStep 1: Add NFS mount
-
Install the required NFS packages:
apt-get install nfs-common -
Create the mount point directory:
mkdir -p /mnt/nfs -
Edit
/etc/fstaband add the following lines (where1.2.3.4is the internal IP of the Services machine):1.2.3.4:/var/opt/gitlab/nfs /mnt/nfs nfs defaults,nfsvers=4,soft,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,noatime -
Mount the share:
mount -a -t nfs
You can check if the mount is working by checking the existence of the
directories builds/, git-data/, shared/, and uploads/ in
/mnt/nfs:
ls /mnt/nfsStep 2: Configure proxied SSL
The load balancer will take care of the SSL termination, so configure nginx to work with proxied SSL.
Follow the instructions to configure proxied SSL.
Step 3: Configure connections to the Services machine
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add the following:## ## Use the NFS mount to store data ## gitlab_rails['uploads_directory'] = '/mnt/nfs/uploads' gitlab_rails['shared_path'] = '/mnt/nfs/shared' gitlab_ci['builds_directory'] = '/mnt/nfs/builds' git_data_dirs({ 'default': { 'path': '/mnt/nfs/git-data' } }) high_availability['mountpoint'] = '/mnt/nfs' ## ## Disable PostgreSQL on the local machine and connect to the remote ## postgresql['enable'] = false gitlab_rails['auto_migrate'] = false gitlab_rails['db_host'] = '1.2.3.4' gitlab_rails['db_password'] = 'DB password' ## ## Disable Redis on the local machine and connect to the remote ## redis['enable'] = false gitlab_rails['redis_host'] = '1.2.3.4' gitlab_rails['redis_password'] = 'Redis password' -
[Only for primary nodes] Add the following to
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:geo_primary_role['enable'] = true -
[Only for secondary nodes] Add the following to
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:geo_secondary_role['enable'] = true geo_postgresql['enable'] = true # TODO set to false when https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/issues/2980 is fixed geo_secondary['auto_migrate'] = false geo_secondary['db_host'] = '1.2.3.4' geo_secondary['db_password'] = 'Geo tracking DB password' Copy the database encryption key. Follow the instructions of Step 1. Copying the database encryption key
Reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect (if you haven't done this yet in previous step).
Restart GitLab to start the processes with the correct connections.
Troubleshooting
HAProxy
You can connect to https://example.com/haproxy?stats to monitor the
load balancing between the Application machines.